Grave’s disease, also known as hyperthyroidism or Graves’ hyperthyroidism, is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the thyroid gland.
the grave disease is one of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism, and it can occur at any age, although it is more common in women and people in their 20s and 30s. The exact prevalence of Grave’s disease is difficult to determine, as it can go undiagnosed or be misdiagnosed due to its wide range of symptoms. However, it is estimated to affect about 1 in 200 people in the United States.
If left untreated, the grave disease can cause a number of serious health problems, including an enlarged heart, osteoporosis, and problems with the eyes. It can also cause a number of uncomfortable or even painful symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, weight loss, heat intolerance, and tremors. With proper treatment, however, most people with Grave’s disease can lead normal, healthy lives.
Early detection and treatment of grave diseases are important for managing the condition and minimizing its potential impacts on the body. If left untreated, Grave’s disease can cause a number of serious health problems, such as an enlarged heart, osteoporosis, and problems with the eyes. It can also cause a number of uncomfortable or even painful symptoms.
Treatment options for the grave disease include medications, radioiodine therapy, and thyroid surgery. The type of treatment that is most appropriate for an individual will depend on a number of factors, including the severity of the condition and the person’s overall health.
By getting an early diagnosis and starting treatment as soon as possible, it is possible to manage the grave disease and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you have any symptoms that may be related to Grave’s disease, or if you have a family history of the condition. Your healthcare provider can help determine the best course of treatment for you.
The main topic of this article is the symptoms of Grave’s disease. grave disease, also known as hyperthyroidism or Graves’ hyperthyroidism, is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the thyroid gland.
The grave disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, and these symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. Some common symptoms of Grave’s disease include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, heat intolerance, and tremors. Other less common symptoms may include goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland), Graves’ ophthalmopathy (eye problems), and skin changes.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of grave disease and to seek medical help if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Early detection and treatment of Grave’s disease can help manage the condition and minimize its potential impacts on the body. In this article, we will explore the most common and less common symptoms of Grave’s disease in more detail.
What is Grave’s disease?
Grave disease, also known as hyperthyroidism or Graves’ hyperthyroidism, is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that plays an important role in regulating the body’s metabolism and energy levels. It does this by producing hormones that help control the body’s use of energy, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
In people with the grave disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells in the thyroid gland, causing it to become overactive and produce too much T4 and T3. This can lead to a number of symptoms and health problems, as the excess hormones can speed up the body’s metabolism and cause various systems to work too quickly.
Grave’s disease can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in women and people in their 20s and 30s. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the thyroid gland. If left untreated, the grave disease can cause a number of serious health problems, including an enlarged heart, osteoporosis, and problems with the eyes. With proper treatment, however, most people with Grave’s disease can lead normal, healthy lives.
The causes of Grave’s disease, including genetics and autoimmune factors
The exact cause of the grave disease is not fully understood, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is known that Grave’s disease tends to run in families, so there is likely a genetic component to the condition. It is also thought that certain environmental triggers, such as infections or stress, may play a role in the development of the condition.
The grave disease is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the thyroid gland. In people with Grave’s disease, the immune system produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland, causing it to become overactive and produce too much thyroid hormone.
While the exact cause of the grave disease is not known, it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. If you have a family history of Grave’s disease or other autoimmune disorders, you may be at an increased risk for developing the condition. It is also important to note that Grave’s disease can occur at any age, although it is more common in women and people in their 20s and 30s.
Common symptoms of Grave’s disease:
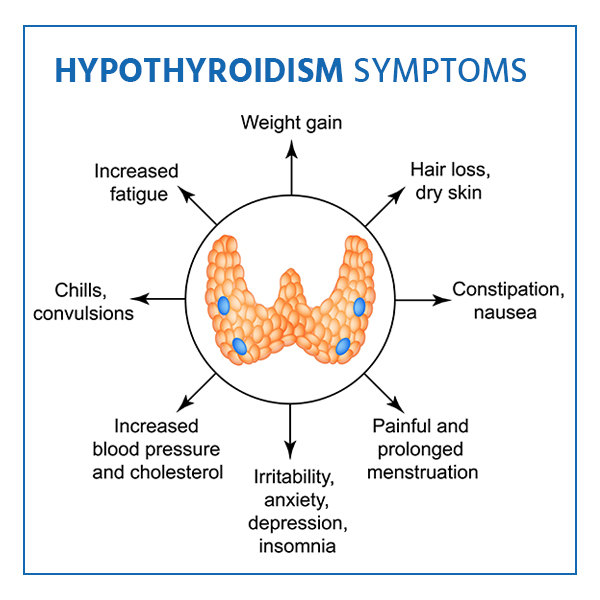
The most common symptoms of Grave’s disease include:
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia): People with Grave’s disease may experience a rapid or irregular heartbeat, as the excess thyroid hormone can cause the heart to work harder and faster.
- Weight loss: Despite an increased appetite, people with Grave’s disease may experience unintended weight loss due to the increased metabolism caused by the excess thyroid hormone.
- Heat intolerance: People with Grave’s disease may feel unusually warm or have an intolerance to heat, as the excess thyroid hormone can cause the body’s metabolism to increase, resulting in an increase in body temperature.
- Tremors: People with Grave’s disease may experience tremors, especially in the hands and fingers, due to the excess thyroid hormone.
- Nervousness and anxiety: The excess thyroid hormone can cause people with Grave’s disease to feel nervous, anxious, or on edge.
- Sweating: People with Grave’s disease may experience excessive sweating due to the increased metabolism caused by the excess thyroid hormone.
- Fatigue: Despite feeling more energized due to the increased metabolism, people with Grave’s disease may also experience fatigue due to the demands on the body’s systems.
- Difficulty sleeping: The excess thyroid hormone can cause people with Grave’s disease to have difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Muscle weakness: People with Grave’s disease may experience muscle weakness, especially in the upper arms and thighs.
- Changes in menstrual cycle: In women, Grave’s disease can cause irregular periods or light menstrual periods.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other conditions as well, and it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Less common symptoms of Grave’s disease:
In addition to the more common symptoms of Grave’s disease, there are also some less well-known symptoms that can occur. These include:
- Goiter: A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, and it can occur in people with Grave’s disease due to the overproduction of thyroid hormone. A goiter may be visible as a swelling in the neck.
- Graves’ ophthalmopathy: This is a condition that affects the eyes and is caused by the immune system attacking the tissues around the eyes. It can cause a number of symptoms, including bulging eyes, dry or red eyes, vision changes, and light sensitivity.
- Skin changes: People with Grave’s disease may experience changes in the texture or appearance of their skin, including thinning or thickening, or the development of fine, brittle hair.
It is important to note that these symptoms may not always occur in people with Grave’s disease, and they can also be caused by other conditions. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis and treatment:
the process of diagnosing Grave’s disease, including physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests:
Grave’s disease is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests.
- Physical exams: A healthcare provider will typically begin by performing a physical exam, during which they will check the thyroid gland for any signs of swelling or enlargement. They may also check for other signs of Grave’s disease, such as a rapid or irregular heartbeat, tremors, and changes in the skin or hair.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help determine the level of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood. In people with Grave’s disease, the levels of thyroid hormones are usually high, while the level of TSH is usually low.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or radioactive iodine uptake tests, can help visualize the thyroid gland and determine how well it is functioning.
It is important to note that there is no single test that can definitively diagnose Grave’s disease. A healthcare provider will typically consider the results of multiple tests, as well as the person’s symptoms and medical history, when making a diagnosis. If you are experiencing symptoms that may be related to Grave’s disease, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
the various treatment options available, including medications, radio iodine therapy, and thyroid surgery:
There are several treatment options available for people with Grave’s disease, and the most appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and the person’s overall health. Treatment options include:
- Medications: There are several medications that can help manage Grave’s disease, including beta blockers, which can help control the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, and anti thyroid medications, which can help slow the production of thyroid hormone.
- Radioiodine therapy: This treatment involves taking a small amount of radioactive iodine, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and helps reduce its activity. This treatment can be effective, but it may take several weeks or months for the full effects to be seen.
- Thyroid surgery: In some cases, thyroid surgery may be recommended to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. This can be an effective treatment for Grave’s disease, but it may also cause side effects, such as low thyroid hormone levels, which will need to be managed with medication.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual needs. Treatment for Grave’s disease may need to be adjusted over time, as the condition can recur or change in severity.
Conclusion:
In summary, Grave’s disease is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. It is an autoimmune disorder, and it can affect people of all ages, although it is more common in women and people in their 20s and 30s. Common symptoms of Grave’s disease include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, heat intolerance, and tremors. Less common symptoms may include goiter, Graves’ ophthalmopathy, and skin changes.
Early detection and treatment of Grave’s disease are important for managing the condition and minimizing its potential impacts on the body. Treatment options include medications, radioiodine therapy, and thyroid surgery. The most appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and the person’s overall health.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of Grave’s disease and to seek medical help if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. By getting an early diagnosis and starting treatment as soon as possible, it is possible to manage Grave’s disease and reduce the risk of complications. If you have any concerns about your thyroid health, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider.
If you have any concerns about your thyroid health, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment. Early detection and treatment of Grave’s disease are important for managing the condition and minimizing its potential impacts on the body.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of Grave’s disease and to seek medical help if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Don’t ignore any persistent changes in your health, as early treatment can make a big difference in managing the condition and reducing the risk of complications.
If you have a family history of Grave’s disease or other autoimmune disorders, you may be at an increased risk for developing the condition. It is a good idea to speak with your healthcare provider about your risk factors and any steps you can take to reduce your risk.
Remember, your healthcare provider is there to help you manage your health and address any concerns you may have. Don’t hesitate to reach out to them if you have any questions or concerns about your thyroid health.
If you or someone you know is at risk for Grave’s disease, we encourage you to share this article with them. Early detection and treatment of Grave’s disease are important for managing the condition and minimizing its potential impacts on the body. By spreading awareness about the symptoms and risk factors for grave disease, we can help more people get the help they need to manage this condition.
If you have any concerns about your thyroid health, we encourage you to speak with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend the appropriate treatment. Don’t ignore any persistent changes in your health, as early treatment can make a big difference in managing the condition and reducing the risk of complications.
If you have a family history of grave disease or other autoimmune disorders, you may be at an increased risk for developing the condition. It is a good idea to speak with your healthcare provider about your risk factors and any steps you can take to reduce your risk.
Remember, your healthcare provider is there to help you manage your health and address any concerns you may have. Don’t hesitate to reach out to them if you have any questions or concerns about your thyroid health.